
User Guide
Contents
PPPoE Internet Sharing with IPNetRouter
- Choosing the Proper Setup Method for
PPPoE Sharing
- PPPoE Dual Ethernet Internet Sharing
- LAN Client Configuration for PPPoE
- Other Configuration Notes For PPPoE LANs
Choosing the Proper Setup Method for
PPPoE Sharing
There are now two classes of PPPoE ("PPP-over-Ethernet")
connection software on Macs – those that use Remote Access
(RA) and those that do not. The instructions in this chapter were
originally written assuming you had an older style PPPoE drivers
that did not use Remote Access. Older style PPPoE connection software
include EnterNet (non-RA version), Sympatico, AccessManager, or
MacPoet. If your DSL Internet connection instead requires Remote
Access (eg Enternet RA or Alcatel USB modem) for high speed access,
read the next few paragraphs and then follow the directions in the
"Internet Sharing using Remote Access
and Ethernet" chapter. MacDSL, T-DSL , and EnterNet (RA
version) use Remote Access for PPPoE connectivity.
We strongly recommend that you download
and install IPNetRouter 1.5 or later for use with PPPoE Internet
sharing. If you must use an older version of IPNetRouter, LAN client
configuration will be more complicated.
If you have a single ethernet configuration then you might not
want to use MacPoet. You can download
the EnterNet client software and try that if you have problems
configuring MacPoet. Read all instructions thoroughly before beginning
an installation.
Although many users have dual ethernet configurations working on
nubus Macs with PPPoE drivers, we have few reports of single
ethernet (one port) nubus Mac sharing their connection. If you manage
to get such a configuration to work, please let us know!
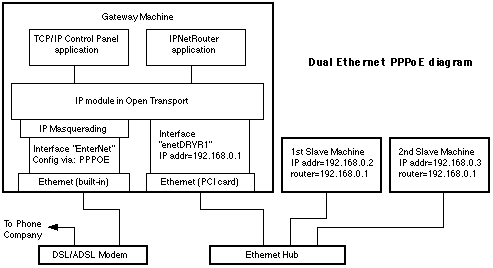
PPPoE Dual Ethernet Internet Sharing
Basic steps to configure IPNetRouter with PPPoE or LANTunnelBuilder
5.0.9a in a dual ethernet setup:
- On the gateway machine, use the TCP/IP control panel to configure
the PPPOE driver for the DSL/ADSL modem as instructed by your
service provider. Make SURE that the "Load Only When Needed"
option is UNCHECKED. (You must be in Advanced User mode to
get to the TCP/IP options. Choose User Mode under the Edit menu
and select Advanced.) If you can already access the Internet from
this machine via your DSL/ADSL modem and you are SURE that the
"Load Only When Needed" option is UNCHECKED in the TCP/IP
control panel, you're ready to proceed to the next step.
IF you are using an older NuBus machine to run IPNetRouter, this
DSL/ADSL modem connection MUST be made into the built-in ethernet
port. With PCI bus machines, the cable/DSL/ADSL modem can be plugged
into either ethernet port.
- Open your PPPoE client and connect to the internet before
launching IPNetRouter. The PPPoE driver must be loaded with
an active connection before IPNetRouter is running. Verify that
you can connect to the internet with a browser and then quit the
browser. If you do not do this first, you may experience problems
configuring IPNetRouter, including crashing and hanging of your
system.
- After connection with the PPPoE client, launch the IPNetRouter
application. Verify that you can still connect to the internet
with a browser and quit the browser before proceeding to the next
step.
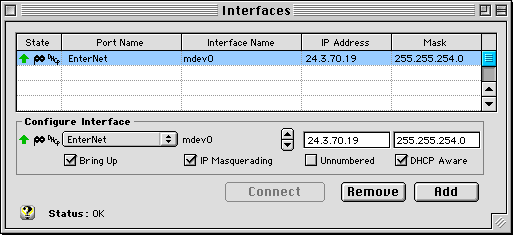
- In the Interfaces window, click on the top row (with your public
IP address on the ethernet port). With this interface selected,
check the "IP masquerading" box, check the the "DHCP
Aware" box, and click Add. You should see a little mask icon
appear in the state column for the PPPOE interface and a DHCP
icon. Notice you need to enable IP Masquerading on the interface
that communicates directly with your DSL/ADSL modem through the
PPPOE driver. Your Interfaces window should now appear similar
to the following (your Port Name, IP address and mask values will
vary depending upon the PPPOE driver you use and the IP and mask
values assigned by your ISP):
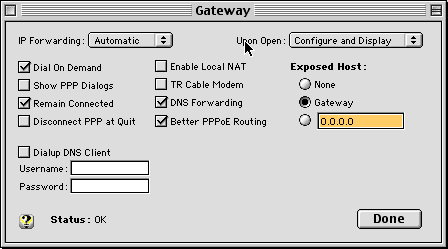
- In IPNetRouter's Gateway window, make sure that IPForwarding
is "Automatic", and that the following are checked:
- "Remain Connected"--if the PPPoE connection times
out while IPNetRouter is running, your system may hang if
you try to reconnect.
- "Better PPPoE Routing" (versions 1.5c12, c14 and
later) or "Limit MTU for PPPoE" (1.5c8-11)
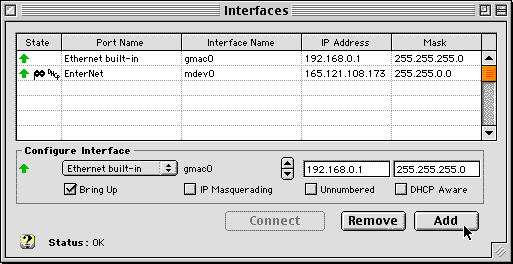
- Next you need to create a 2nd IP interface on your other Ethernet
port. Continue to work in the Interfaces window using the "Configure
Interface" input area just below the main display grid. Select
the other ethernet port from the popup menu under the Port Name
column. The corresponding interface name is entered for you automatically
(you should not need to change this). Enter a local IP Address
and Mask. We suggest 192.168.0.1 and 255.255.255.0 respectively.
Only the "Bring Up" checkbox should be checked. Press
Add. You should see all the values you just entered appear in
a new row in the main Interfaces table.

- Select SaveAs from the File menu
to name and save your configuration. Launch the PPPoE client and
then double click on this config file anytime you want to startup
IPNetRouter with this configuration. Your gateway should now be
working! If it doesn't work right away, try restarting once to
give Open Transport a chance to rebuild your TCP/IP stack with
the supplied Proxy module inserted.
- See Slave Configuration below.
Top
Single Ethernet Configuration
for PPPoE
For the PPPoE Single Ethernet configuration you will be following
many of the steps used in the dual ethernet example above. This
example works with LanTunnelBuilder (LTB), EnterNet 1.09 and Sympatico/Access
Manager, both derivatives of the LTB software. The following is
for an iMac running OS 9 but should work on any PCI Mac and some
nubus configurations:
- Read the introduction to PPPoE configuration.
Carefully follow steps 1-5 for dual ethernet
PPPoE configuration.
- Verify that you can connect to internet with a browser and quit
the browser.
- To configure your LAN interface, create a second interface (EnterNet)
should appear by itself initially) in the Interface window using
the Ethernet built-in interface as shown in the diagram...
- Follow steps 7-8 for dual ethernet
PPPoE configuration.
Top
LAN Client ("Slave") Configuration
With PPPoE
Now each slave machine on your LAN needs to be configured to take
advantage of this new gateway:
- Each slave machine needs its own unique IP address from the
same private sequence that the gateway is using. In the above
example the gateway is at 192.168.0.1, so your slaves should each
use a unique addresses like 192.168.0.2, or 192.168.0.X where
X is anything from 2 up to 255.
- All the slave machines need to be told to use the gateway machine
(192.168.0.1) to access the Internet. So set the Default Gateway
(router) parameter of all slaves to 192.168.0.1
- You can use the IPNetRouter IP address as the Name Server address
in each of the clients (e.g. 192.168.0.1). Just make sure that
the DNS forwarding option is checked in the Gateway window of
IPNetRouter. (you MUST be running IPNetRouter v1.4.8 or later
for DNS forwarding). Otherwise you need to enter the true Name
Server for your ISP in each of the client machines.
- With the dual ethernet setup only, you can use the DHCP server
within IPNetRouter to configure your client machines. This may
be easier than individually and manually addressing each of the
client machines on your private network. Using the DHCP server
within IPNetRouter is quite simple: just open the DHCP window
and click the DHCP Server On checkbox and click Done. There are,
however, many other options you can configure with the DHCP
server. Please see the Help window in the DHCP window for
more information. You should never enable IPNetRouter's DHCP
server feature in a single ethernet configuration with a cable/xDSL
modem--there is a limitation in the DHCP standard that prevents
this from working correctly.
- When using IPNetRouter prior to 1.5,
you must install IPNetTuner
to set the Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) on each of your Mac
client machines. Set the MTU size to somewhere between 1350 and
1482 bytes on each Mac. Regedit can be used to set the MTU on
Windows clients. Skip having to do client configuration for MTU
by checking the "Better PPPoE Routing" checkbox in the
Gateway options window of IPNetRouter 1.5 or later. "Better
PPPoE Routing" negotiates the MTU with your clients automatically.
Top
Other Configuration Notes For
PPPoE LANs
Email and Browser applications running on the client machines should
have their servers (such as mail and news servers) set to the standard
values specified by your provider. You may, however, have to use
FULLY SPECIFIED DOMAIN NAMES for Mail servers when accessed from
your client machines (e.g. instead of just using "mail"
for the SMTP mail server, you might have to fully specify the name
like "mail.srst1.fl.home.com"). Also make sure the slaves
each have a unique IP address and will use the gateway (typically
192.168.0.1) as their default gateway. On a Mac use the TCP/IP or
MacTCP Control Panel, on Windows
use the Network Control Panel.
If you need to determine the IP address of the default Name Server
(DNS) which your ISP has you currently using, you can use the IPNetRouter
log window, the PPPoE client info window, or the tools in IPNetMonitor
to determine this IP address. From the gateway machine, launch IPNetMonitor
and open the NSLookup Window (Name Server Lookup). From the NSLookup
window, open the Ping window (Cmd-T), this will invoke a ping test
to your default Name Server, used by NSLookup. Your default Name
Server address will be visible in the Ping window. You could then
use this IP address in each of your client machines... but just
using your gateway's local LAN address with DNS forwarding is normally
much easier.
IP Addressing: I chose the example IP addresses from network
192.168.x.x because this network range is reserved for private Internets
(see RFC 1918).
In order to route IP datagrams between two networks, each network
must normally have its own network number (the most significant
part of the IP address logically ANDed with the network mask). If
you wish to follow the suggested example, each machine on your ethernet
LAN must have a unique address from network 192.168.0.x (192.168.0.1,
192.168.0.2, 192.168.0.3, etc.). The Macintosh running IPNetRouter
(192.168.0.1 in this example) becomes the default router or gateway
for the other machines on your ethernet LAN. You can use a different
network address in this range, 192.168.111.x or 192.168.3.x, for
example, instead of 192.168.0.x.
See the Troubleshooting
and OS 9 Compatibility section, Read Me and release notes documents
included in your installation folder, and the FAQ
page on our web site for more info on configuring your LAN with
IPNetRouter.
Top
|

 Privacy
Policy
Privacy
Policy  Contact
Us
Contact
Us
 Privacy
Policy
Privacy
Policy  Contact
Us
Contact
Us